As most of you know DOM refers to DOCUMENT OBJECT MODEL which is nothing but the Nested Tree structure of the HTML / XML code.
→ Each node in the tree is an Object representing HTML elements.
→ DOM allows HTML code to connect with JavaScript, DOM can be manipulated directly (i.e) documet.getElementById().
The workflow of Web Browers

→ DOM tree itself is constructed by the rendering engines.
→ Now the CSS is applied to HTML creating the render tree.
→ Now the render tree is painted in the browser.
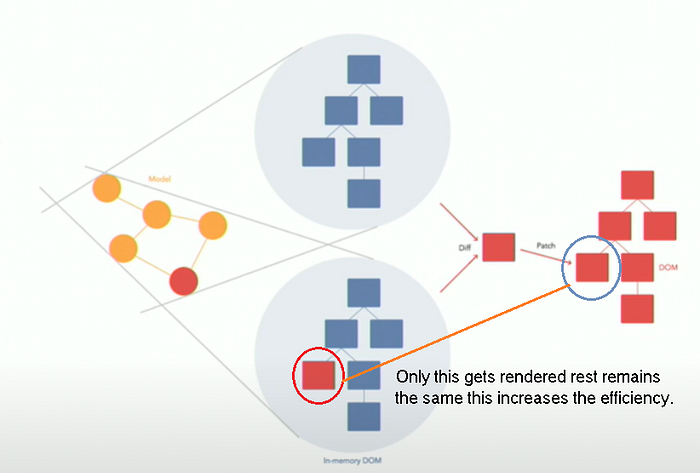
Now Updating this tree becomes Expensive, to overcome this frameworks like React, Vue, Angular, etc uses Virtual DOM.
VIRTUAL DOM
→ Instead of changing all the changes to the real DOM first, these are applied to the virtual DOM.
→ virtual DOM is not rendered directly, It is stored in the memory of the framework used.
→ virtual DOM is a lightweight representation of real DOM.
→ It is just a plain JavaScript object tree.
How Virtual DOM Works
→ The changes made first updates the virtual DOM where now the differences between both real DOM and virtual DOM are rendered in the real DOM.
→ It does render everything so virtual DOM is fast and efficient
SHADOW DOM
→ Shadow DOM allows creating the Custom Components.
→ It allows a component to have it's very own “shadow” DOM tree, that can’t be accidentally accessed from the main document, may have local style rules, and more.
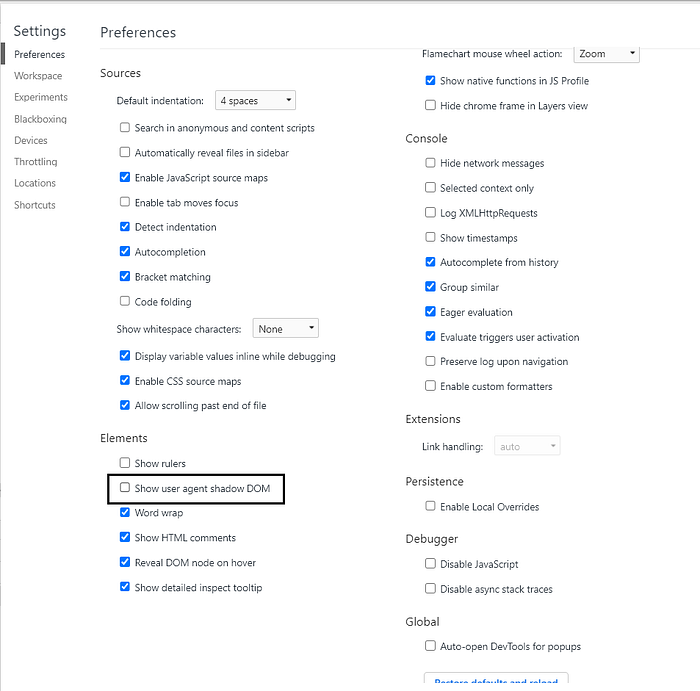
→ To inspect the shadow dom code in Chrome
Settings → Elements → (check) Show user agent shadow DOM
→ Have their own ids space,
→ Invisible to JavaScript selectors from the main document, such as querySelector,
→ Use styles only from the shadow tree, not from the main document.

0 likes
2 comments
Like
Jul 7, 2024
hsy
Dec 17, 2024
i been identity theft by Audrey Turner Rison this is Tonya Voss
Add your comment